SATELLITES
In 2016, it has continued working on the H30W-6 and Amazonas 5 satellites, whose launches are scheduled for 2017, and that will embark demonstrators using photonic technology.
In this sense, the Hispasat 30W-6 satellite will implement, for the first time, an extended Ka band receiver demonstrator whose performances are comparable to the current microwave receivers available in the market. This will in the future significantly reduce mass and volume in the entry section by reducing the number of units required compared to the existing technology today.
In the Amazonas 5 satellite, a flight demonstrator will be implemented to validate radio frequency optical link distributions for use in future missions as part of the satellite payload. The unit internally transmits 10 MHz and 10 GHz signals on fiber optic links without interacting with the payload on the satellite. It is intended to evaluate the performance of the links monitoring the power consumption and phase deviation telemetry, among others, during the first year of life.
In addition, the H36W-1 incorporates RedSAT, an advanced regenerative payload consisting of a novel active antenna with reconfigurable beams that, together with the on-board processor, will improve the efficiency and services offered by the satellite. The antenna can be controlled electronically from the Earth and reoriented at any point during the lifespan of the satellite, granting it the flexibility to adapt its coverage to mission changes that may occur after launch, while still in orbit.
The on-board processor is a further step in the evolution of satellites, which can greatly simplify network architecture by performing in space a part of the processing usually carried out on Earth. It can simultaneously process up to four 36 MHz transponders, correcting possible signal degradations and transmitting them without errors, leading to a more robust and higher quality communications system that enables signal reception with small-diameter antennas.
This satellite also incorporates an experimental GPS receiver that will demonstrate the feasibility of using GPS signals at 36,000 Km in height in order to determine with high precision the position of the satellite in its orbit.
Within the initiative started in 2015 aimed at reducing procurement costs, in 2016 HISPASAT completed the first stage of defining a high-throughput satellite (HTS). Contacts with the industry enabled the company’s needs to be aligned with the technological developments that will ensure standout services in very competitive markets.
PROJECTS
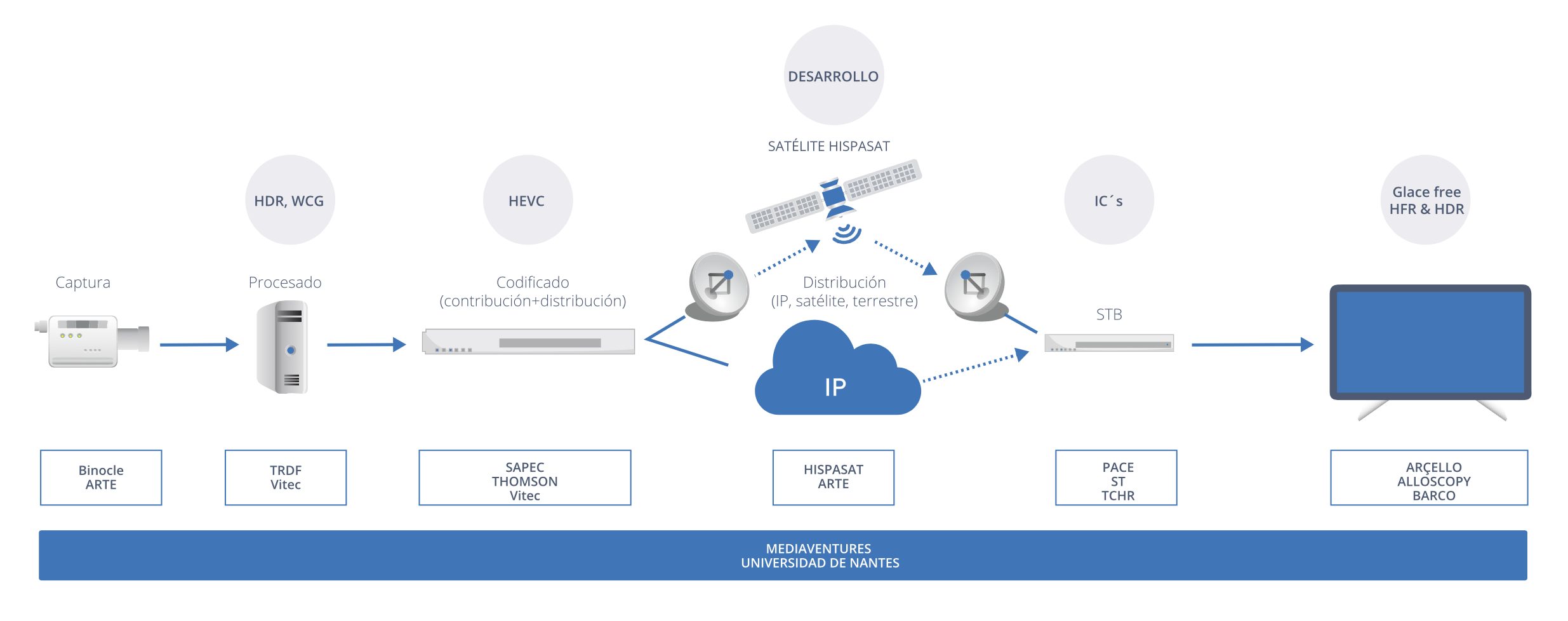
ULTRA HIGH DEFINITION 4K
UHDTV is, without a doubt, one of the most promising technologies in the eld of advanced television systems. This technology provides a fourfold increase in resolu- tion over standard high de nition and provides an image sharpness that gives the user a high sense of quality. Satellites are the ideal platform for UHDTV services given their high bandwidth, which is necessary in order to transmit this large amount of information in high quality.
During 2016, HISPASAT carried out numerous initiatives to help develop technologies that would bring UHDTV into homes. Among some of the most noteworthy acti- vities in this area, HISPASAT has maintained a speci c 4K channel in Europe and North America, using its Hispasat 30W-5 and Amazonas 3 satellites, respectively, and provided a demonstration using HDR (High Dynamic Range) encoding. Moreover, the company has continued to promote the technology in events such as the Hispasat 4K Festival and live broadcasting of events in UHD, among others.
With regard to results, last year a demonstration was made of the use of 4K transmission of a documentary about the Prado Museum via satellite, while in the reception a subtitled or dubbed HD video can be reproduced using picture-in-picture (a video within another larger video) at the same time as the 4K documentary is running. One of the keys to this project was the synchronisation of the contents on broadcast networks in di erent formats.
At the same time, HISPASAT continues to work with manufacturers and distributors to develop technology that facilitates the widespread implementation of this type of content, such as new coding systems, as well as medium term improvements such as 8K.
HYBRID NETWORKS AND CONNECTED TV
In the last few years, HISPASAT has actively participated in the study of new coding technologies and the interconnectivity of satellite, fibre and cable networks, making use of Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), with a special focus in 2016 on hybrid architecture (OTT, multicast or streaming satellite).
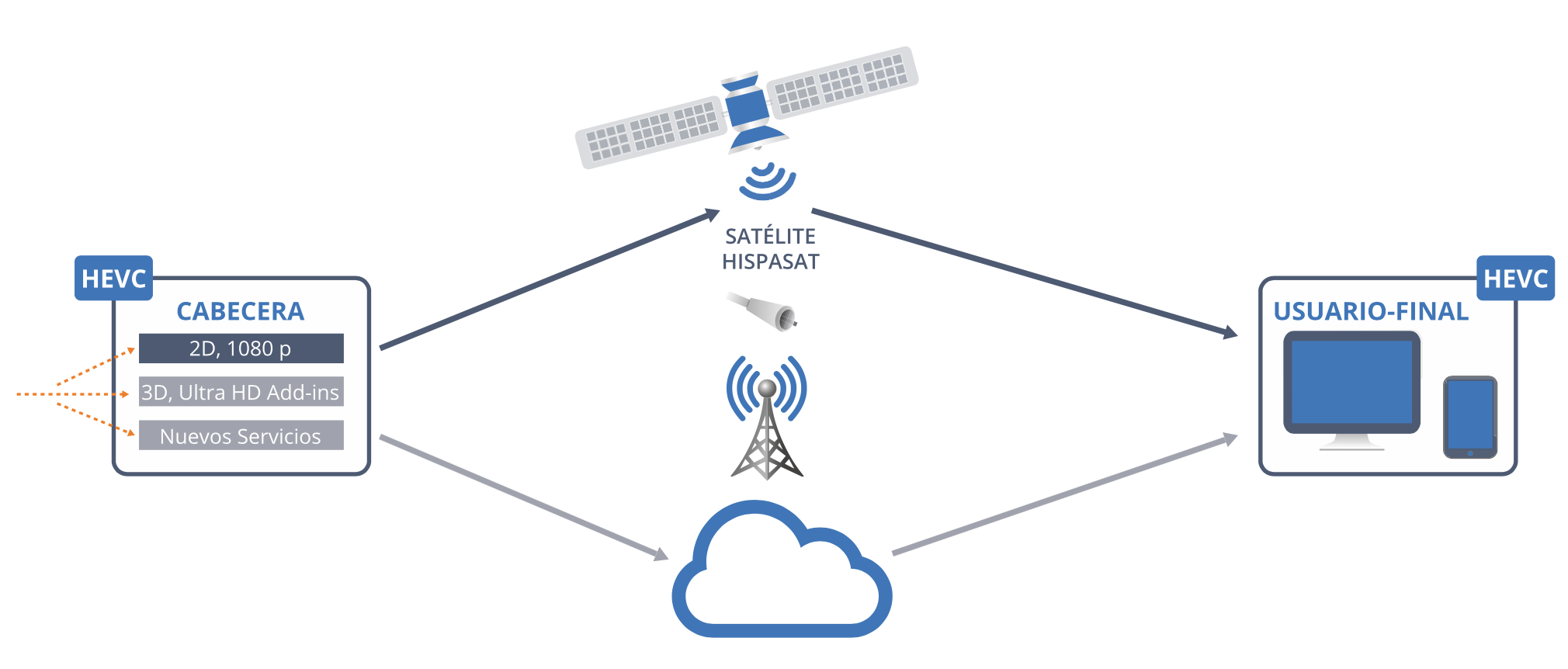
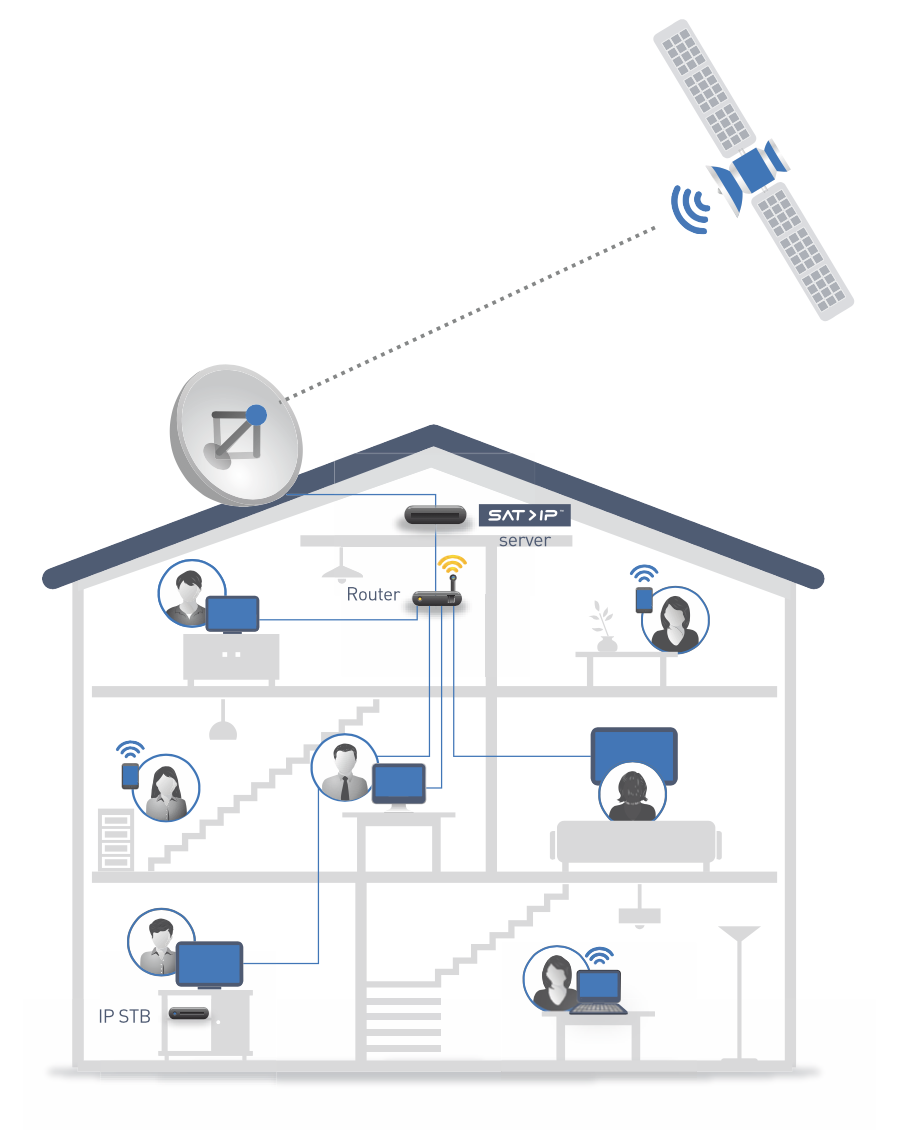
In 2016, in the eld of connected TV, HISPASAT continued working on promoting SAT-IP technology, a system that allows satellite signals to be distributed over an IP network in the home, closing the gap between the multiscreen world and satellites. This idea, simultaneously developed by HISPASAT in the SATURNO project and by SES, led to the creation in 2015 of an important alliance between these two companies called the SAT>IP Alliance.
In other areas of the audiovisual and hybrid market, initial analyses have been made on the possible applications of using satellites in virtual reality.
OTHER CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS
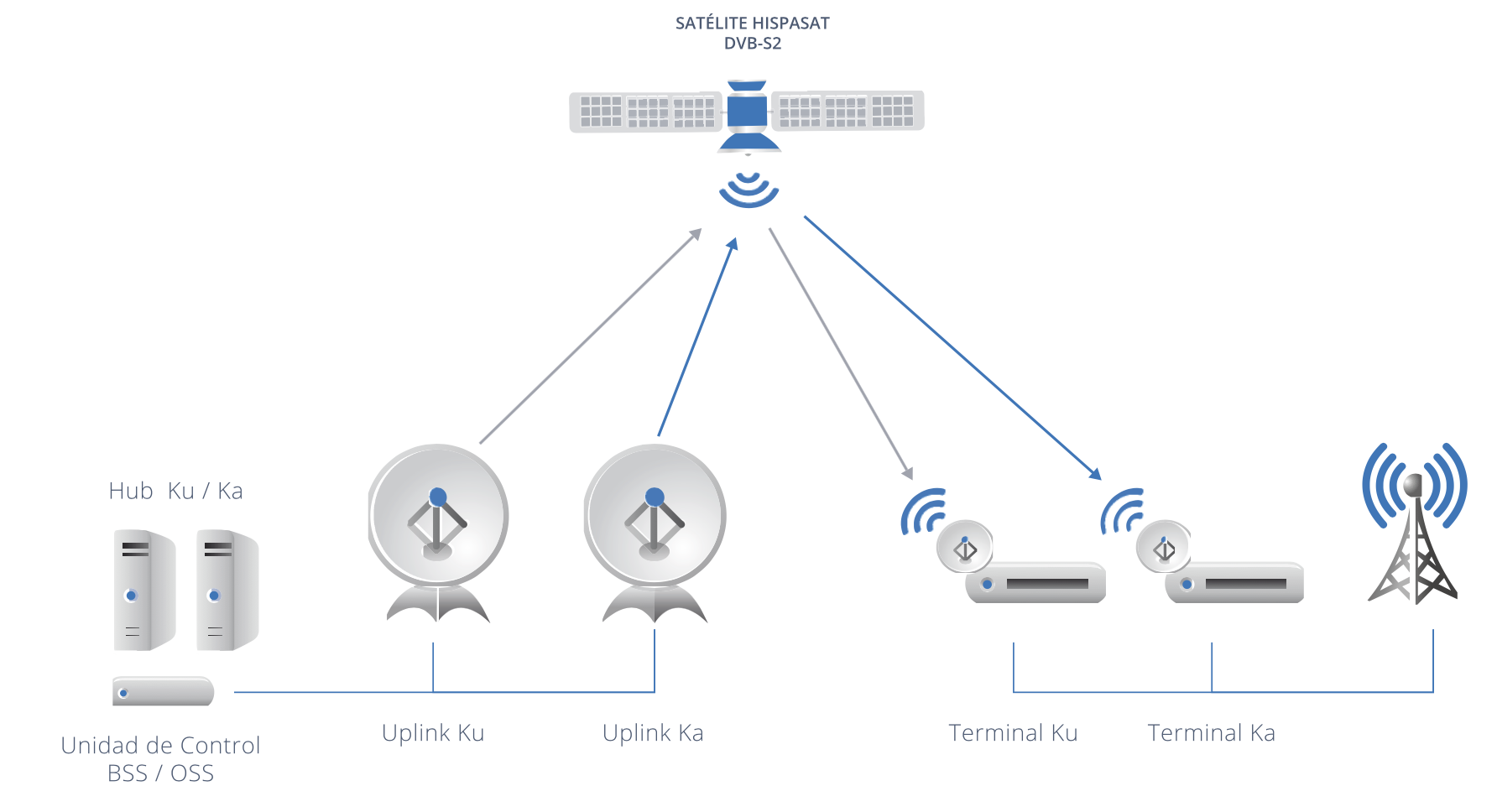
KU/KA HYBRID BACKHAUL
In 2016, work was done on defining an architecture of a pilot test for a Ku/Ka hybrid backhaul. Due to its greater resistance to weather alterations, the Ku band is used for voice traffic, ensuring continuity at all times, while the Ka band, thanks to its greater space capacity, is applied to data traffic in order to achieve greater speed, equivalent to current LTE/4G networks, and this solution has been presented to several possible clients, with whom tests are expected for 2017.
INTERNET OF THINGS (loT)
The need to digitally interconnect all objects to the Internet, from a wind mill at a wind farm to any home appliance, was the concept that spawned the Internet of Things (IoT).
This need is related to the high demand for which satellites provide an important value, given their fast deployment, coverage of 100% of the territory and their robustness.
Throughout 2016, HISPASAT studied solutions and possible applications of the IoT in which satellites may participate, as well as possible partners, and help provide a competitive solution adjusted to possible customer needs, with special interest in the search for low-cost and small user equipment which provides an optimal service quality.
In 2017, testing will begin on these types of solutions as a complement to analyses carried out in 2016, with the objective of providing a commercial solution in the near future.
EMERGENCIES AND SECURITY
In 2016, HISPASAT continued to develop an efficient solution for emergencies and security called ONTIME. This solution will be used to collect, process, display and communicate emergency information for both land and mobile units.
Throughout the year, pilot tests were carried out, such as the one which was performed during the presentation of Rozas Airport in Lugo, in which a quick-deploy antenna was used to transmit video signal recorded by a drone over the beach, shown in real time at the airport, transmitting this video signal via satellite.
In 2017, as a result of a collaborative effort with Inaer, a global leader in emergency air services and a partner of HISPASAT, the company seeks to implement a solution for security and emergencies throughout all Spanish territory and for all administrations, security forces and public and private administrators who demand emergency solutions.
MOBILITY
TRAINS
After a commercial agreement in 2015, HISPASAT became one of the providers assigned to provide connectivity to the Renfe’s AVE train feet. Then, a pilot project
was developed, led by HISPASAT, on board one of the trains to o er a solution that would allow a passenger to connect to the Internet, access exclusive multimedia content and live on-demand television, all on one device or on different devices, all while travelling over 300 Km/h. Providing such services is highly complex, especially considering that trains pass by many obstacles on their journey.
This type of solution requires a hybrid system that allows cellular connectivity and connectivity via satellite, depending on tra c type and quality. Only when these technologies are used together can all passengers access quality service while travelling at high speeds. Moreover, a very speci c antenna is needed for the satellite reception.
During 2016, the company worked on implementing the commercial service in Renfe AVE trains, which began last November.
HISPASAT collaborated with Aicox and Indra to develop and implement an antenna that is compatible with all types of high-speed trains, and that has characteristics allowing for greater service efficiency and availability.
Likewise, HISPASAT, together with CTTC (Centre Tecnològic de Telecomunicacions de Catalunya), continued working on the development of the project to include voice backhaul via satellite in high-speed trains, which would enable access to the aforementioned services as well as the ability to make and receive telephone calls on any part of the route, which is nowadays very limited with current cellular networks.
PLANES
A speci c case of mobility is that of space capacity for communication services for UAVs. An Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) is an aircraft with no crew on board and equipped with satellite communications systems. These systems are used both for remote control and collected image or data transmission.
For these types of services, HISPASAT, along with top manufacturers, is searching for solutions managing the environment in which missions are carried out and the connectivity of the payload transported by aircraft. This search includes the development of new payloads in specific satellites for the product, along with the optimisation of the equipment on board to lighten its weight and enable the incorporation of ever lighter UAVs.
AUTOMOBILES
HISPASAT is participating in the project Sat2Car, along with companies PSA Peugeot Citro, EGATEL, ALTIA and QUOBIS. The main objective of this project is the development and validation of an integral system of mobile services and applications on vehicles via satellite through the development of an end-to-end technological platform which allows for one-way and two-way broadband applications with high added value, enabling the exchange of real time information and communication between vehicles and service providers.
NEW NETWORK DESIGN TOOL
Throughout 2016, HISPASAT, along with members of the Higher Technical School of Telecommunications Engineering of the Universidad Politécnica de Madrid and GMV, developed an automated IT tool to create more precise and automated network designs, with features facilitating the adaptation of designs to meet any customer requirement.
The tool is mounted on a web application and therefore access is immediate once the user is validated. Moreover, it has a pro ling system which enables its distribution on di erent levels, both inside and outside HISPASAT.
The most developed line during 2016 was in the automation of the necessary calculations for presenting and de ning networks to HISPASAT’s clients. Moreover, great e orts were made in the representation of results based on public geographic maps which enable installers to carry a veri cation tool for features in their own smartphone and compare them to with the measures taking place in real time.
Throughout 2017, new improvements in representation and access to HISPASAT’s customers and users will be included, which will make this tool more powerful and useful.


